In this article we provide information regarding latest Class 7 Computer Notes for April Month – Navodaya TGT Computer Science (CS) 2024-25.
Class 7 Computer Notes for April Month – Navodaya TGT CS
We are using source for Syllabus – Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti Perspective Academic Planning Split of Syllabus 2024-25.
We are giving to the Point Notes for the Students.
Thanks Me Later
For the April Month Notes – Class 7 Computer Subject
Unites we covered in Notes
- Introduction to Network
- What is a Network ?
- Types of Network
- What is Network Cabling?
- Types of Cables used in Networks
- Computer Network Components
- Introduction to Internet
- What is an Internet ?
- Application of Internet
So Let’s Discuss the One by one.
Introduction to Network
What is Computer Network ?
A group of computer which are connected to each – other for the purpose of sharing their resources is called computer network.
First Computer Network – ARPANET
The U.S. Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first public packet-switched computer network. It was first used in 1969
Characteristics of Computer Network
- Resource Sharing
- Communication Speech
- Backup
- Scalability
- Reliability
- Software & Hardware Sharing
- Security
Network Devices
HUB, Switch, Bridge, Gateway, Modem. Router, Repeater etc.
Network Types
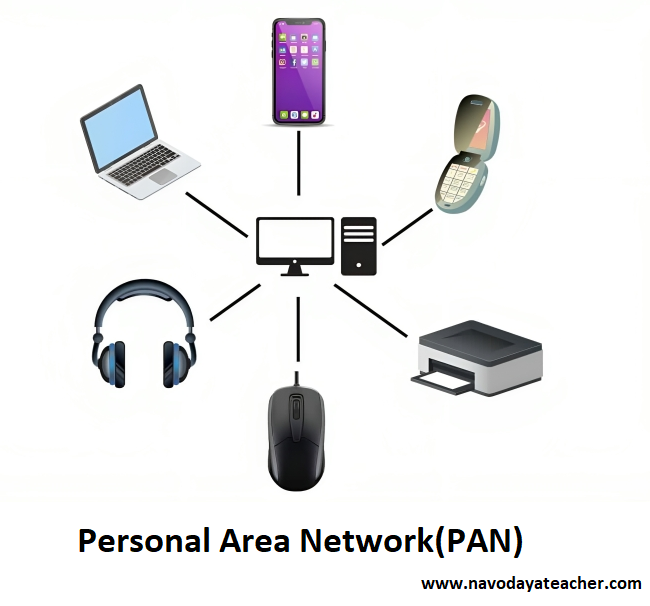
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
- Range : <10m
- Use – Home (For Personal Use)
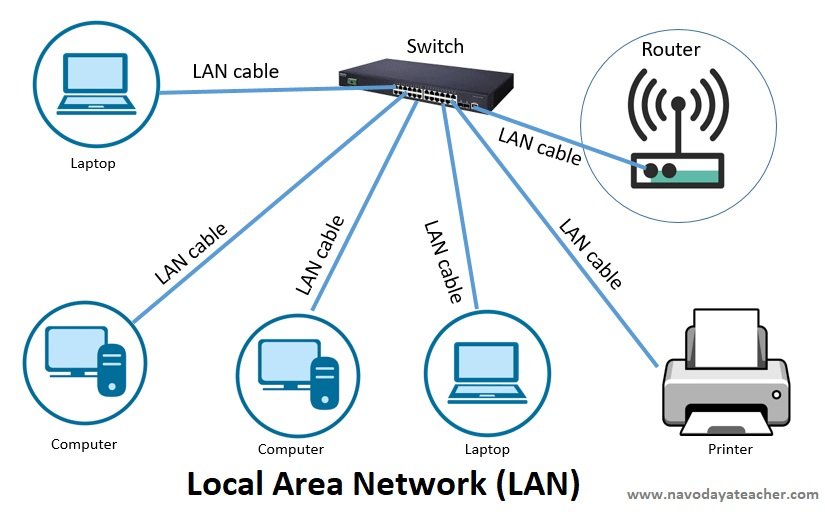
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- Range : <150m
- Use – Office (Building)
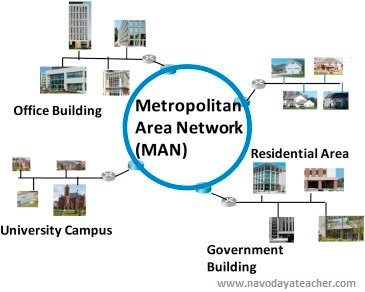
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- Range : <50km
- Use – Within City
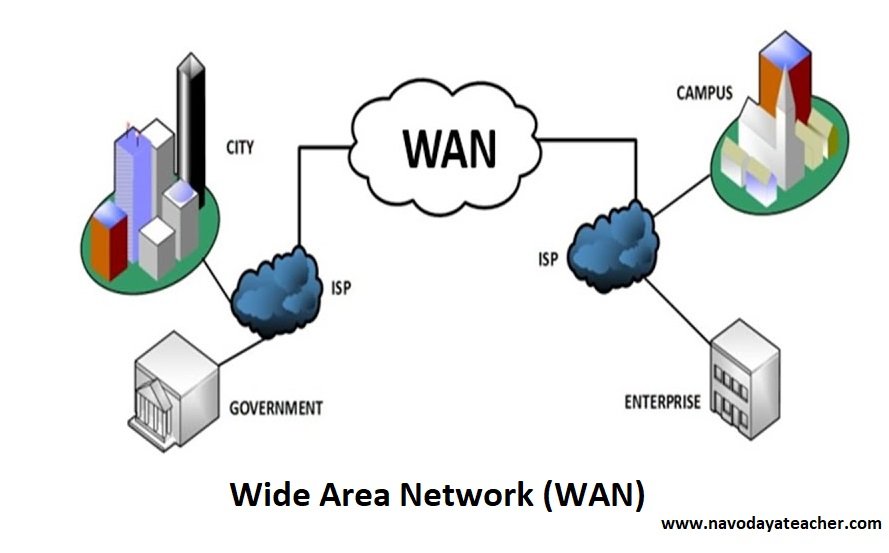
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
- Range : Not Fixed
- Use – Use for Countries or All around world.
Advantages :
- Open to Everyone
- File sharing
- Security
- Easy to add new devices
- Backup Storage.
Disadvantage :
- Network device required
- Virus attack
- Required Hander
- High Speed Internet
- Server
Difference Between LAN, MAN & WAN in Computer Networks
| LAN | MAN | WAN |
| LAN stands for Local Area Network | MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network | WAN stands for Wide Area Network |
| It is used for building like offices. | It is used for city like Ahmedabad. | It is used for countries. |
| Transmission speed of data is high. | Transmission speech of data is average. | Transmission speed of data is low. |
| LAN network range is 0 to 150m | MAN network range is 5 to 50km | Not fixed |
| LAN Network ownership is private | MAN network ownership is Private or Public | WAN network ownership is also Private or Public |
| Easy to Maintain | Difficult to maintain than LAN | Also difficult to maintain than MAN as well as LAN |
| LAN network error rate & setup cost is low | MAN network error rate & setup cost is average | WAN network error rate & setup cost is very high. |
What is Network Cabling ?
Network Cables :
To connect two or more computers or networking devices in a network, network cables are used.
Types of Cables used in Networks
- Coaxial Cable
- Twisted Pair Cables
- Fiber Optic Cable
1. Coaxial Cable
This cable contains a conductor, insulator, braiding & sheath.
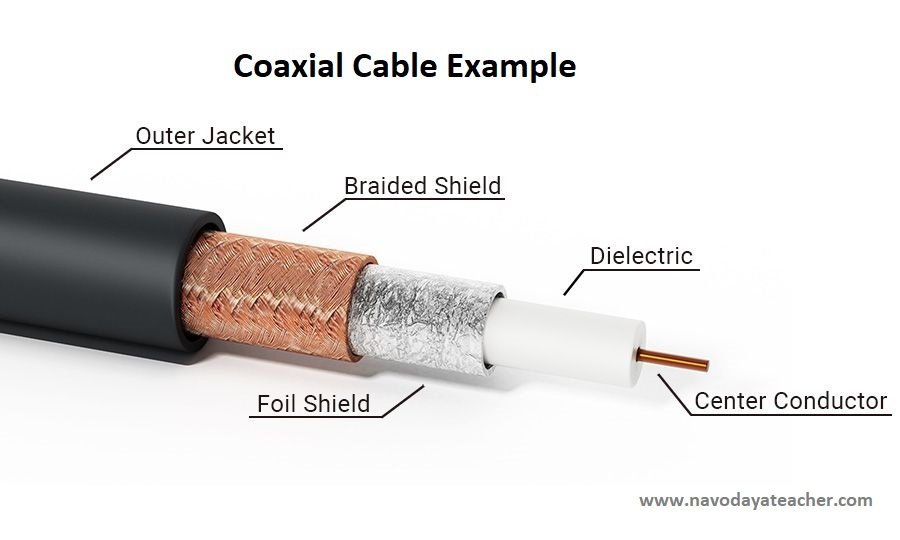
Coaxial Cable Conductor types (1. Thick Coaxial – 10Base5 – 2-5mm thick) (2. Thin Coaxial (10Base2 – 6mm thick)
10BaseT : 10 = 10 MBPS, Base = Half Duplex, T = Transmission Distance
Categories of Coaxial Cables
| Types | Impedance | Used |
| RG-59 | 75 | Short-distance cable TV |
| RG – 58 | 50 | Thin Ethernet Cable |
| RG – 11 | 50 | Thick Ethernet Cable |
Applications of Coaxial Cables
- Analog telephone networks
- Digital Telephone networks
- Cable TV networks
- Traditional Ethernet LANs
2. Twisted-pair cables
It was primarily developed for computer networks. This cable is also known as Ethernet Cable. almost all modern LAN computer networks use this cable.

TIA / EIA specifies standards for the twisted-pair cable. First standards were released in 1991. Known as TIA/EIA 568.
These standards have been continually revised to cover the latest technologies and developments of the transmission media.
Twisted-pair cables
- UTP – Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP Cables)
- STP – Shielded twisted-pair (STP Cables)
Connector Used –
| Perticulars | RJ-45 | RJ-11 |
| Application | Ethernet Cables | Connecting telephone wires |
| Number of wires | 8 | 4 |
| Size | Big | Small |
| Bandwidth | 10 GBPS over Ethernet | 24 MBPS |
3. Fiber Optic Cable / Optical Fiber Cable
This cable consists of core, cladding, buffer, and jacket.
The core is wrapped in the cladding; Cladding is wrapped in the buffer, and the buffer is wrapped in the jacket.
Structure of Fiber Optics
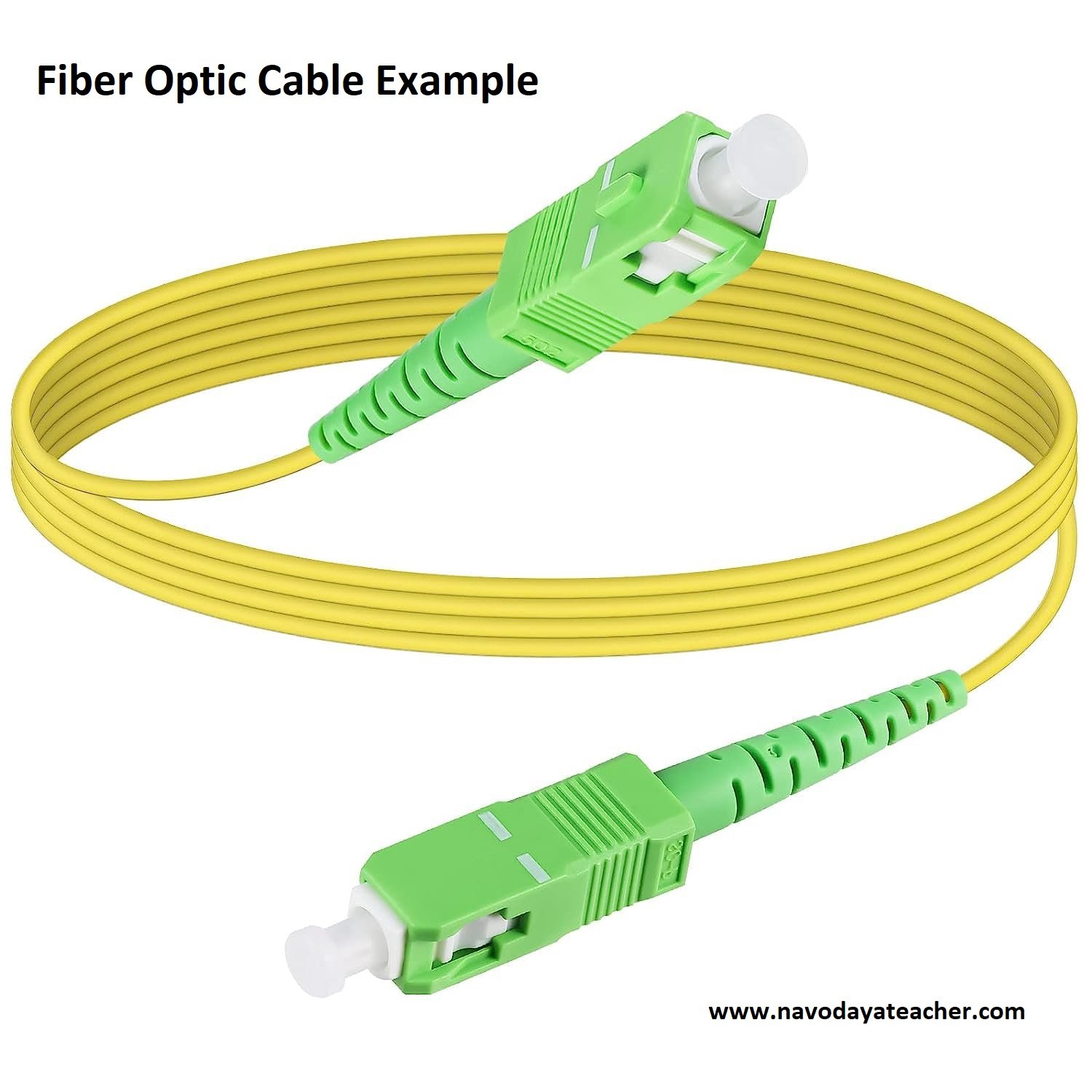

This cable can transmit data over a long distance at the highest speed. It can transmit data up to 40 Kilometers at the speed of 100 GBPS.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables
- Fiber optics support a higher capacity (Fiber Cables rated at 10Gbps, 40Gbps, and 100 Gbps are standard)
- Transmit signals over much longer distances
Two common types of fiber cables
- Single mode Fiber (SMF)
- Multi mode giber (MMF)
Multimode cable has a larger diameter. Single mode can provide more distance, but it is more expensive.
Introduction to Internet
The Internet –
The Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices.
The Internet is used for many things, such as electronic mail, online chat, file transfer, and the interlinked web pages and other documents of the World Wide Web.
What is Internet ?
Internet is a network of networks that is used to interlinked many different types of computers all over the world.
The Internet is a vast network that connects computers all over the world. Through the Internet people can share information and communicate from anywhere with an internet connection.
Application of Internet
- Education
- Business
- E-commerce
- Media and Entertainment
- Social Networking
- Forum
- Health and Fitness
Disadvantage of Internet
- Virus Threat
- Spamming
- Cyber Crime
- Cyber Terrorism
- Time Wasting
World Wide Web
The World Wide web (‘www’ or ‘web’ for short) is a collection of webpages found on this network of computers. your web browser uses the internet to access the web.
We are continuing from July Month.
Thanks to Beloved Readers.